Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a powerhouse nutrient crucial for energy, brain function, and red blood cell formation. It’s water-soluble, meaning your body doesn’t store much of it—and deficiency can lead to fatigue, nerve damage, and mood issues. Whether you’re plant-based or just looking to boost your wellness, this guide covers what B12 does in the body, signs of deficiency, best sources, and how to supplement effectively if needed.
What Is Vitamin B12 and What Does It Do?
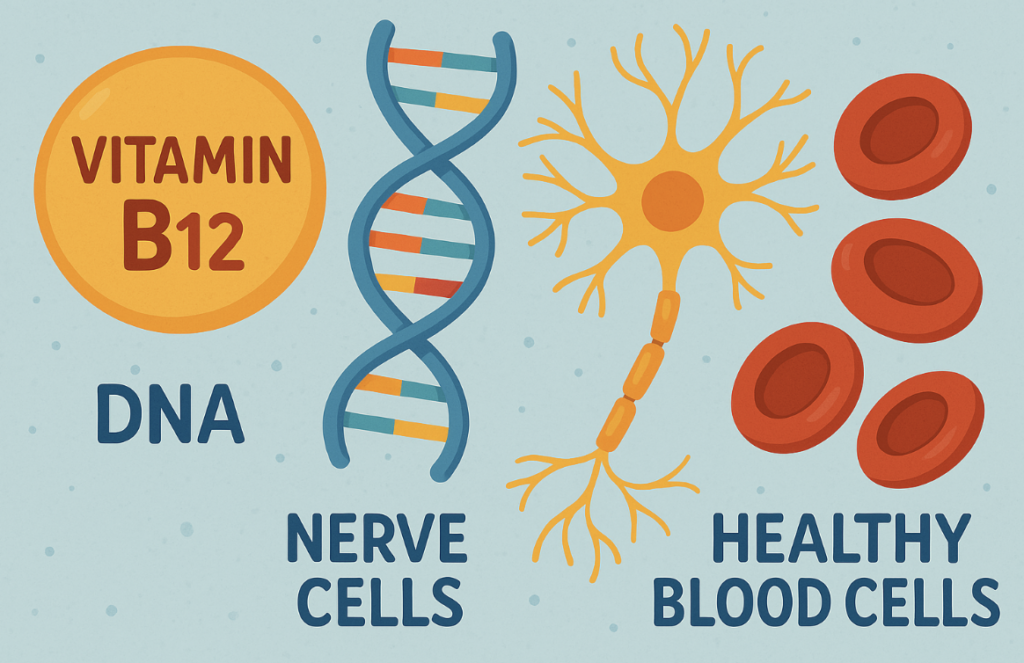
Vitamin B12 helps your body make DNA, nerve cells, and healthy blood cells. It’s also vital for brain health and neurotransmitter function.
✔ Key Functions of B12:
- Assists in red blood cell formation and oxygen delivery
- Helps maintain the protective sheath around nerves (myelin)
- Supports brain function and mood regulation
- Plays a role in DNA and RNA synthesis
- Helps convert food into usable energy (metabolism)
💡 Did You Know? B12 is unique among vitamins because it contains cobalt, a trace element essential for its biological activity.
Top Health Benefits of Vitamin B12
✔ 1. Boosts Energy and Reduces Fatigue
Low B12 interferes with oxygen transport, leading to sluggishness and weakness.
✔ 2. Supports Brain Health and Focus
Adequate B12 levels help prevent memory problems, cognitive decline, and brain fog.
✔ 3. Enhances Mood and Mental Health
B12 is involved in serotonin production and has been linked to lower risk of depression.
✔ 4. Prevents Anemia
A lack of B12 leads to megaloblastic anemia, causing fatigue and shortness of breath.
✔ 5. Supports Pregnancy and Fetal Development
B12 helps in fetal brain and nervous system development and reduces risk of birth defects.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency

⚠️ Common Symptoms:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Difficulty walking or poor balance
- Pale skin or jaundice
- Mood changes like irritability or depression
- Cognitive issues (memory loss, brain fog)
💡 High-Risk Groups:
- Vegans and vegetarians (B12 is mainly found in animal products)
- People over 50 (reduced absorption with age)
- Individuals with GI conditions (e.g., celiac, Crohn’s)
- Those taking antacids or metformin long-term
Best Dietary Sources of B12
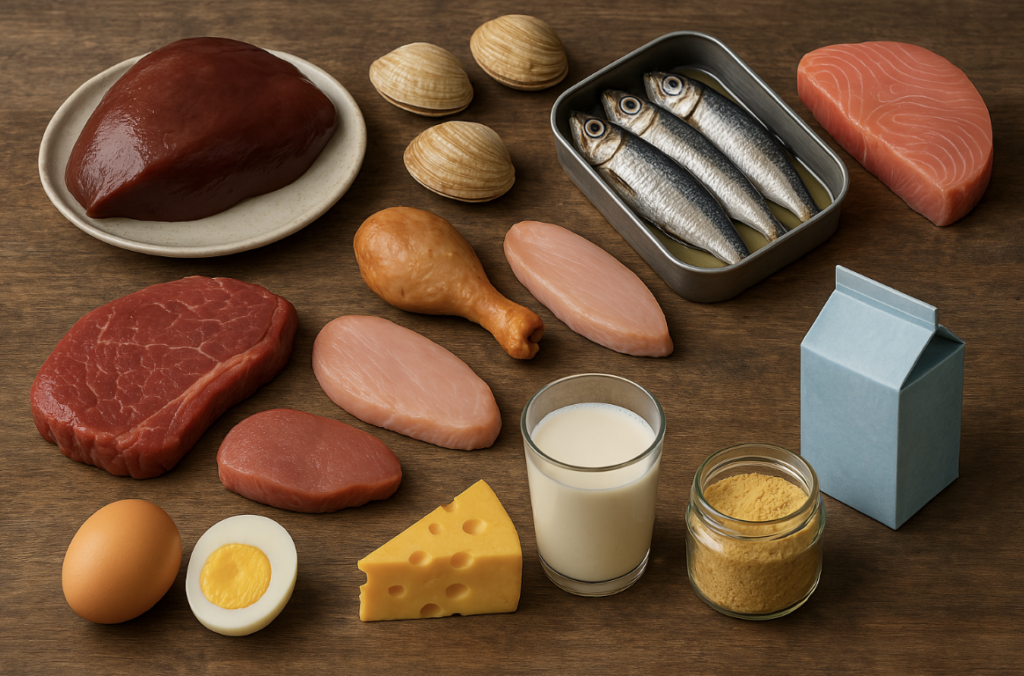

🥩 Animal-Based:
- Liver and organ meats
- Clams, sardines, and tuna
- Beef, chicken, and turkey
- Eggs and dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt)
🌱 Plant-Based:
- Fortified plant milks, breakfast cereals, and nutritional yeast
💡 Tip: Read food labels carefully—look for “cyanocobalamin” or “methylcobalamin” on fortified products.
Recommended Daily Intake (RDI)
- Adults (19+): 2.4 mcg/day
- Pregnant women: 2.6 mcg/day
- Breastfeeding women: 2.8 mcg/day
- Higher doses may be needed for those with absorption issues or on restrictive diets
Vitamin B12 Supplementation
💊 Best Forms:
- Cyanocobalamin: Most common and stable
- Methylcobalamin: Natural and may be better absorbed in the brain
✔ Supplement Types:
- Tablets, sublinguals, sprays, or injections (for severe deficiency)
- Multivitamins may include B12, but not always enough for vegans/deficient individuals
⚠️ Too Much B12?
- No known upper limit toxicity, but high doses can cause mild digestive upset in some people
Pros and Cons of B12
✔ Pros:
- Essential for brain, nerve, and blood health
- Supports mood and energy levels
- Easy to supplement, especially for vegans
⚠️ Cons:
- Only found naturally in animal products
- Can be masked by folate supplementation (delays diagnosis of deficiency)
- Absorption issues are common in older adults
Vitamin B12 is vital for your energy, focus, and neurological health. Deficiency is more common than you think—especially in plant-based eaters and older adults. Focus on getting enough from diet or supplements to protect your brain, boost your mood, and keep your body functioning at its best.
Read more on how iron supports energy and oxygen levels
Learn more about vitamin B12 from Harvard Health
